APT Scanner
Threat Scanner
APT Scanner
Threat Scanner
Advanced Persistant Threat Scanner (APT Scanner)
The APT Scanner is the core component of our Compromise Assessment Service. It can be used to continuously monitor networks, systems and applications for signs of advanced persistent threat (APT) activity. The APT scanner detects suspicious behavior patterns, unusual network activity or indicators that could point to an APT attack. By professionally evaluating the scan results, our cyber defense experts are able to efficiently and reliably detect compromised IT systems in your infrastructure.
Play it safe and detect compromised systems in your infrastructure before major damage occurs.

Are you asking yourself whether your company has already been attacked and whether your protective measures are really effective? Find out!
At SECUINFRA, we have a passion for detecting attacks and helping our customers defend against them. In cooperation with Nextron-Systems GmbH, we have developed a solution that supports you in doing just that, because so-called Advanced Persistent Threats remain undetected for a long time and can cause major damage.
An APT scanner can use various techniques to detect these attacks. This includes monitoring network traffic, analyzing log files, detecting anomalies in user and system behavior and using machine learning algorithms to identify suspicious activity.
How an APT scanner works
How does an APT scanner detect a cyber attack? In contrast to classic antivirus software, an APT scanner does not search for fragments of malicious code, but rather for traces of an attack, so-called Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), as in a forensic investigation. To do this, the APT scanner uses a set of rules containing Indicators of Compromise (IOCs).
This set of rules is applied to various artifacts in a system (files, folder structures, running processes, memory contents, log data…) to search for traces of past or ongoing cyberattacks.
Thanks to the international cooperation of the cyber defense community, new cyber attacks are continuously analyzed, indicators of compromise are derived and stored as new rules in the APT scanner.
As a result, the APT scanner becomes increasingly precise over time and, in contrast to classic antivirus software, has an extremely high detection rate of compromised systems.
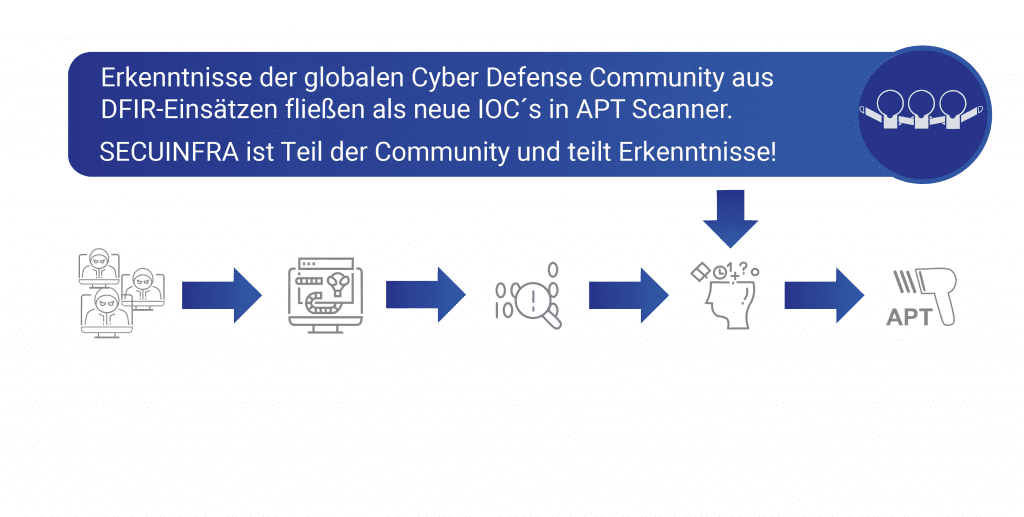
In a cyber attack, attackers or an APT group use various tools and techniques to achieve their goals. These tools and techniques inevitably leave detectable traces on the compromised systems. Clever attackers will cover some of these traces, but it is not possible to remove all traces!
By analyzing compromised IT systems and collecting evidence, it is possible to derive Indicators of Compromise (IOCs).
These Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) are entered into the rules of the APT scanner and used for future scans.
If an attacker uses similar tools and techniques, these are detected very efficiently by the APT scanner and the time-consuming forensic investigation can be accelerated enormously.
Application examples of an APT scanner
Compromise Assessment
The APT Scanner is the core component of our Service Compromise Assessment. By professionally evaluating the scan results of the APT scanner, our cyber defense experts are able to efficiently and reliably detect compromised IT systems in your infrastructure.
Digital Forensics
In the area of digital forensics, our cyber defense experts use APT scanners to quickly gain an initial overview of the extent of a cyber attack. In addition, initial conclusions can be drawn about the course of the crime. Both are essential for the complete investigation of an external cyber attack or internal misconduct.
Incident Response
The primary objective of incident response is to restore IT operations as quickly as possible. By using an APT scanner, our cyber defense experts achieve exactly the necessary speed. With the help of the APT scanner, they quickly gain an overview of the extent of a cyber attack at the beginning of their mission.
The most important FAQ from the APT Scanner section
An Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) is an advanced and persistent cyber threat that is usually directed against specific, high-value targets. An APT is typically a long-term cyber attack that aims to infiltrate a network and remain undetected in order to steal or manipulate data rather than cause quick and immediate damage.
The “advanced” component of APT refers to the high technological capabilities and skills of the attackers. They often use sophisticated methods, including zero-day exploits and social engineering, to achieve their goals.
“Persistent” refers to the persistence and long-term nature of this type of attack. APT attackers are usually very patient and can remain active in a network for months or even years to achieve their goal.
Finally, the term “threat” indicates that it is an active and serious threat that can cause considerable damage, especially if it is not recognized and averted in time.
APT attacks are often well-funded and can originate from criminal organizations or even state-sponsored actors. They often target governments, military installations, large corporations, and other high-value targets.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APT) are complex, multi-stage attacks. This type of attack is usually targeted and can go on for months or even years. Here is a basic overview of how such attacks can take place:
- Identifying and researching the target: First, the attackers identify their targets and research them in detail to find vulnerabilities. These can be organizations or individuals. They gather as much information as possible to plan their attack strategy.
- Infiltration: After an attack plan has been created, the attackers attempt to penetrate the target’s network. Various methods can be used for this, e.g. phishing attacks, the use of zero-day exploits or the use of malware.
- Movement within the network (lateral movement): Once they have gained access to the network, they try to expand their presence by moving to other systems. This process is known as lateral movement. The aim is to gain access to valuable data or resources and take control of the network.
- Persistence: APT attackers try to make their presence in the network as inconspicuous and permanent as possible. Various techniques can be used for this purpose, such as installing backdoors, creating fake user accounts or exploiting system vulnerabilities.
- Exfiltration: Once the attackers have gained access to the desired information, they begin exfiltration, i.e. they transfer the data out of the network unnoticed.
- Concealment: Finally, the attacker will try to cover all traces of his activities in order to avoid detection at a later date.
It is important to note that APT attacks are difficult to detect and resolve due to their complexity and targeting. Therefore, a proactive security strategy based on threat intelligence, regular security audits and continuous monitoring is crucial.
Detecting and defending against Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) requires a multi-layered security strategy, as APTs are highly sophisticated and often bypass traditional security measures. Below are some important steps for detecting and defending against APTs:
- Network monitoring and analysis: Continuous monitoring and analysis of network traffic is critical to detect unusual activity or deviations that could indicate an APT attack.
- Threat intelligence: Threat intelligence services can provide organizations with up-to-date information on known APTs, their modus operandi and how to detect them.
- Security assessments and penetration tests: Regular security assessments and penetration tests can uncover vulnerabilities that could be exploited by APTs before they do.
- Incident Response Plan: A good incident response plan is crucial for a quick and effective response to security incidents and can help limit the damage of an APT attack.
- Employee training: Since human error often plays a role in APT attacks, employees should be trained in security best practices, including how to recognize phishing attempts and how to use network resources safely.
- Patches and updates: Security patches and updates should be applied immediately to fix known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by APTs.
- Use of advanced security tools: Some advanced security tools such as Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) can help detect and defend against APTs.
These strategies can help organizations protect their networks from APTs, but it’s important to note that no strategy can guarantee 100% security. It is important to remain vigilant and follow the latest trends and developments in cyber security.
Below you will find some examples of Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs).
- Stuxnet: Perhaps the most well-known example of an APT was Stuxnet, a malicious program specifically designed to attack Iranian nuclear facilities. It is widely believed that this attack was carried out by the United States and Israel.
- Operation Aurora: This series of attacks in 2009 targeted several large technology and defense companies, including Google and Juniper Networks. It is suspected that these attacks were controlled by China.
- APT28 (Fancy Bear) and APT29 (Cozy Bear): These two Russian hacker groups are known for their advanced and long-lasting attacks. They are suspected of being behind the attacks on the US Democratic Party in 2016.
- The Equation Group: This sophisticated hacker group is associated with the US National Security Agency (NSA). It is known for its advanced cyberattack capabilities and was first identified by the Russian IT security company Kaspersky Lab in 2015.
- Lazarus Group: This North Korean hacking group has been linked to a number of APTs, including the infamous hacking attack on Sony Pictures in 2014 and the attempted bank robbery in Bangladesh in 2016.
These examples show how APTs are capable of threatening both national security interests and corporate networks at the highest level. They underline the need for an effective cyber security strategy to protect against such threats.
Identifying the specific actors behind advanced persistent threats (APTs) can be a challenge, as attackers often go to considerable lengths to disguise their identity and location. Nevertheless, many APT attacks can be assigned to specific groups or even states based on the technology used, the targets and other indicators.
APT actors are often well financed and highly qualified. In many cases, these are state-sponsored hacker groups or units working on behalf of a particular country. They carry out these attacks in order to gain economic, political or military advantages by stealing information, undermining infrastructures or spreading disinformation.
There are also cases where APT attacks are carried out by criminal organizations. These groups may carry out such attacks for a variety of reasons, such as financial gain, competitive advantage or simply to cause chaos.
It is important to note that mapping APT attacks is a complex process that often requires a combination of technical analysis and intelligence work. In addition, false flags are sometimes used, with attackers trying to make their attacks appear to be carried out by another group or country in order to create confusion and disguise their own identity.
An APT scanner in the context of cyber security is a tool or system designed to detect and analyze advanced persistent threats (APTs). These scanners are designed to identify advanced, persistent and targeted cyber threats.
An APT scanner can operate at different levels of a network and analyze different types of data to detect signs of APT activity. This can include monitoring network traffic for unusual patterns or activity, checking system logs for signs of intrusion attempts or scanning files for possible malware.
Some APT scanners use advanced technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence to better detect potential threats and adapt to new tactics and techniques used by attackers.
It is important to note that APT scanners are only one part of a comprehensive security strategy. They can help detect and analyze threats, but cannot prevent all types of cyber attacks. They should therefore always be used in combination with other security measures such as firewalls, anti-virus programs, secure software development and security training for employees.
An Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) scanner is a tool that scans networks for traces of APT activity. Such scanners use a combination of different techniques and methods to detect and isolate potential threats. This is how they usually work:
- Signature-based detection: Many APT scanners have a database of known threat signatures that they use to look for matches in network traffic or on host systems. If a match is found, an alarm is triggered.
- Anomaly detection: APT scanners can also detect anomalous behavior that indicates a potential threat. This can be, for example, unusually high data traffic, suspicious login attempts or unexpected changes to system files.
- Sandboxing: Some APT scanners use sandboxing techniques to run potentially malicious files or programs in an isolated environment and monitor what they do. This can help identify malicious activity that might otherwise have gone undetected.
- Threat intelligence: Many APT scanners also integrate threat intelligence services that provide constantly updated information on new and emerging threats. This information can be used to improve the scanner’s detection performance and react more quickly to new threats.
- Forensic analysis: If an APT infection is suspected, the scanners carry out a detailed examination. They collect data and logs for further analysis to determine the extent of the attack and identify possible entry points.
- Reporting and alerting: Once a potential threat has been identified, APT scanners provide detailed reports and alerts. These usually contain information about the type of threat, its effects and recommendations for remedial action.
It is important to note that no APT scanner can guarantee 100% security, as APTs are inherently difficult to detect. They should therefore be considered as part of a comprehensive security strategy that also includes other measures such as staff training, strict access controls and regular security checks.
Companies need an APT scanner for various reasons:
- Threat detection: An APT scanner helps detect Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) that can bypass traditional security measures. APTs are often very good at hiding in the network and remaining undetected.
- Protection of sensitive data: APTs often target the theft of sensitive information. An APT scanner can help prevent the intrusion of such threats and thus ensure data protection.
- Prevent downtime: A successful APT attack can lead to significant business interruptions. By detecting and responding to such attacks early, an APT scanner can help prevent downtime.
- Adherence to compliance regulations: Strict data security and data protection regulations apply in many industries. An APT scanner can help meet compliance requirements by helping to keep networks secure.
- Reputation protection: Data breaches can significantly damage a company’s reputation. An APT scanner can help to prevent such breaches and thus protect the company’s good reputation.
- Cost savings: While deploying an APT scanner requires an investment, the cost of recovering from a successful APT attack, including downtime, data loss and penalties for compliance violations, can be significantly higher. Therefore, the use of an APT scanner can lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
Do you have any further questions about using an APT scanner? Then contact us directly!
That's why SECUINFRA
- Damage minimization
Prevent major damage by detecting compromised systems at an early stage. Since 2010, SECUINFRA’s cyber defence experts have been searching for and finding compromised systems on a daily basis and helping to minimize the damage.
- Reliability
Play it safe and have your most critical systems scanned regularly by SECUINFRA’s cyber defense experts for Indicators of Compromise (IOC). We reliably detect compromised systems in your infrastructure.
- Efficiency
APT scanners are by far the most reliable and efficient technology for detecting compromised IT systems. Increase your cyber resilience through the reliability of APT scanners and save costs through the efficiency of the technology.
Here you can get in touch with us!
Contact form end of page
Contact form at the bottom of the page
"*" indicates required fields
Our portfolio
©2024 SECUINFRA GmbH. All rights reserved.








